벨먼-포드 알고리즘
벨먼-포드 알고리즘(영어: Bellman-Ford algorithm)은 가중 유향 그래프에서 최단 경로 문제를 푸는 알고리즘이다. 이때 변의 가중치는 음수일 수도 있다. 데이크스트라 알고리즘은 벨먼-포드 알고리즘과 동일한 작업을 수행하고 실행속도도 더 빠르다. 하지만 다익스트라 알고리즘은 가중치가 음수인 경우는 처리할 수 없으므로, 이런 경우에는 벨먼-포드 알고리즘을 사용한다.
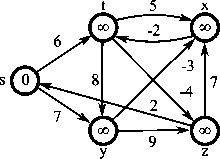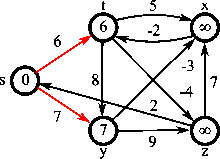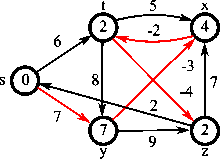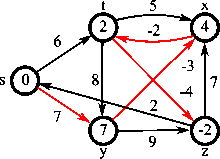 | |
| 분류 | 최단 경로 문제 |
|---|---|
| 자료 구조 | 그래프 |
| 최악 시간복잡도 | |
| 최선 시간복잡도 | |
| 공간복잡도 | |
V와 E가 각각 그래프에서 꼭짓점과 변의 개수라고 한다면, 벨먼-포드 알고리즘의 실행시간은 이다.
의사코드 (Pseudo-code)
편집 // 그래프의 자료구조 정의
record vertex {
list edges
real distance
vertex predecessor
}
record edge {
node source
node destination
real weight
}
function BellmanFord(list vertices, list edges, vertex source) // This implementation takes in a graph, represented as lists of vertices // and edges, and modifies the vertices so that their distance and // predecessor attributes store the shortest paths.
// Step 1: 그래프 초기화
for each vertex v in vertices:
if v is source then v.distance = 0
else v.distance := infinity
v.predecessor := null
// Step 2: 이완 작업 반복
for i from 1 to size(vertices):
for each edge uv in edges:
u := uv.source
v := uv.destination // uv is the edge from u to v
if v.distance > u.distance + uv.weight
v.distance := u.distance + uv.weight
v.predecessor := u
// Step 3:
for each edge uv in edges:
u := uv.source
v := uv.destination
if v.distance > u.distance + uv.weight
error "Graph contains a negative-weight cycle"
실제 프로그래밍 언어로 구현한 소스 코드
편집#define INFINITY ((1 << (sizeof(int)*8-2))-1)
typedef struct
{
int source;
int dest;
int weight;
}Edge;
void BellmanFord(Edge edges[], int edgecount, int nodecount, int source)
{
int i,j ;
int* distance = malloc(nodecount*sizeof(int));
for(i = 0; i < nodecount; i++)
{
if(i == source) distance[i] = 0;
else distance[i] = INFINITY;
}
for(i = 0; i < nodecount; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < edgecount; j++)
{
/*
* Note that INFINITY is actually a finite number in this code, so because of overflow
* "distance[edges[j].source] + edges[j].weight" can be a very small number,
* in fact smaller than "distance[edges[j].dest]".
*
* One solution is to skip the following if-statement,
* if "distance[edges[j].source]" == INFINITY
*/
if(distance[edges[j].dest] > distance[edges[j].source] + edges[j].weight)
{
distance[edges[j].dest] = distance[edges[j].source] + edges[j].weight;
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < edgecount; i++)
{
if(distance[edges[i].dest] > distance[edges[i].source] + edges[i].weight)
{
printf("Error occurred. Negative edge weight cycles detected");
break;
}
}
for(i = 0; i < nodecount; i++)
{
printf("The shortest distance between nodes %i and %i is %i\n", source, i, distance[i]);
}
}
참고 문헌
편집- Richard Bellman: On a Routing Problem, in Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 16(1), pp.87-90, 1958.
- Lestor R. Ford jr., D. R. Fulkerson: Flows in Networks, Princeton University Press, 1962.
- Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001. ISBN 0-262-03293-7. Section 24.1: The Bellman-Ford algorithm, pp.588–592.


