사용자:배우는사람/문서:Urinary bladder
| Urinary bladder | |
|---|---|
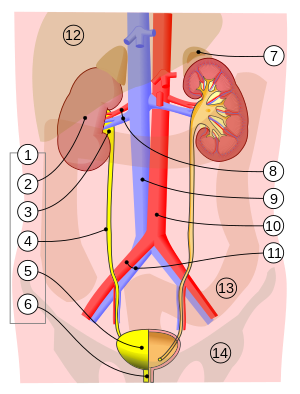 1. Human urinary system: 2. Kidney, 3. Renal pelvis, 4. Ureter, 5. Urinary bladder, 6. Urethra. (Left side with frontal section) 7. Adrenal gland | |
 Male Bladder Makeup | |
| 정보 | |
| 발생기 구조 | urogenital sinus |
| 동맥 | Superior vesical artery Inferior vesical artery Umbilical artery Vaginal artery |
| 정맥 | Vesical venous plexus |
| 신경 | Vesical nervous plexus |
| 림프 | external iliac lymph nodes, internal iliac lymph nodes |
| 식별자 | |
| 라틴어 | vesica urinaria |
In human anatomy, the urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination. A hollow[1] muscular, and distensible (or elastic) organ, the bladder sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
Bladders occur throughout much of the animal kingdom, but are very diverse in form and in some cases are not homologous with the urinary bladder in humans.
Embryologically, the human urinary bladder is derived from the urogenital sinus and, it is initially continuous with the allantois. In males, the base of the bladder lies between the rectum and the pubic symphysis. It is superior to the prostate, and separated from the rectum by the rectovesical excavation. In females, the bladder sits inferior to the uterus and anterior to the vagina. It is separated from the uterus by the vesicouterine excavation. In infants and young children, the urinary bladder is in the abdomen even when empty.[2]
Detrusor muscle
편집The detrusor muscle is a layer of the urinary bladder wall made of smooth muscle fibers arranged in spiral, longitudinal, and circular bundles. When the bladder is stretched, this signals the parasympathetic nervous system to contract the detrusor muscle. This encourages the bladder to expel urine through the urethra.
For the urine to exit the bladder, both the autonomically controlled internal sphincter and the voluntarily controlled external sphincter must be opened. Problems with these muscles can lead to incontinence. If the amount of urine reaches 100% of the urinary bladder's capacity, the voluntary sphincter becomes involuntary and the urine will be ejected instantly. [출처 필요]
The urinary bladder usually holds 300-350 ml of urine; a full adult bladder holds about 500mL of urine, 15 times its empty volume. As urine accumulates, the rugae flatten and the wall of the bladder thins as it stretches, allowing the bladder to store larger amounts of urine without a significant rise in internal pressure.[3]
The desire to urinate usually starts when the bladder reaches around 25% of its working volume. At this stage it is easy for the subject, if desired, to resist the urge to urinate. As the bladder continues to fill, the desire to urinate becomes stronger and harder to ignore. Eventually, the bladder will fill to the point where the urge to urinate becomes overwhelming, and the subject will no longer be able to ignore it.
Since the urinary bladder has a transitional epithelium, it does not produce mucus.[4]
Fundus
편집The fundus of the urinary bladder is the base of the bladder, formed by the posterior wall. It is lymphatically drained by the external iliac lymph nodes. The peritoneum lies superior to the fundus.
Urination frequency
편집Urination frequency refers to the number of times someone urinates. Males with an enlarged prostate urinate more frequently.
Urinary volume
편집The bladder can hold about 500 ml of urine. [출처 필요]
Innervation
편집The bladder receives motor innervation from both sympathetic fibers, most of which arise from the hypogastric plexuses and nerves, and parasympathetic fibers, which come from the pelvic splanchnic nerves and the inferior hypogastric plexus.[5]
Sensation from the bladder is transmitted to the CNS via general visceral afferent fibers. GVA fibers on the superior surface follow the course of the sympathetic efferent nerves back to the CNS, while GVA fibers on the inferior portion of the bladder follow the course of the parasympathetic efferents.[5]
Disorders
편집Disorders of or related to the bladder include:
- Bladder cancer
- Bladder exstrophy
- Bladder infection
- Bladder spasm
- Bladder sphincter dyssynergia, a condition in which the sufferer cannot coordinate relaxation of the urethra sphincter with the contraction of the bladder muscles
- Bladder stones
- Cystitis
- Hematuria, or presence of blood in the urine, is a reason to seek medical attention without delay, as it is a symptom of bladder cancer as well as bladder and kidney stones.
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Overactive bladder, a condition which affects a large number of people.
- Urinary incontinence
- Urinary retention
See also
편집References
편집- ↑ Howard A. Werman, Keith J. Karren.
- ↑ Moore, Keith L.; Dalley, Arthur F (2006). 《Clinically Oriented Anatomy》 5판. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- ↑ Marieb, Mallatt. 〈23〉. 《Human Anatomy》 5판. Pearson International. 700쪽.
- ↑ Chin T, Liu , Tsai H, Wei C (September 2007). “Vaginal reconstruction using urinary bladder flap in a patient with cloacal malformation”. 《Journal of Pediatric Surgery》 42 (9): 1612–5. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.04.040. PMID 17848259.
- ↑ 가 나 Moore, Keith; Anne Agur (2007). 《Essential Clinical Anatomy, Third Edition》. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 227–228쪽. ISBN 0-7817-6274-X.
External links
편집- Histology - KUMC epithel-epith09 "Urinary Bladder"
- Anatomy photo: Urinary/mammal/bladder/bladder1 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis - "Mammal, bladder (LM, Medium)"
- 틀:IowaHistologyInteractive
- Anatomy photo:43:07-0100 - SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: The Urinary bladder"
- Anatomy photo:44:04-0103 - SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Male Pelvis: The Urinary bladder"
Additional images
편집-
Structure of the penis
-
Organs of the female reproductive system.
-
Coronal section of pelvis, showing arrangement of fasciæ. Viewed from behind.
-
Dissection of side wall of pelvis showing sacral and pudendal plexuses. (Bladder visible at lower left.)
-
The peritoneum of the male pelvis.
-
Median sagitta section of male pelvis.
-
Male pelvic organs seen from right side.
-
Median sagittal section of female pelvis.
-
The interior of bladder.
-
Vertical section of bladder wall.
-
Fundus of the bladder with the vesiculæ seminales.
-
Vertical section of bladder, penis, and urethra.
-
Female pelvis and its contents, seen from above and in front.
-
Topography of thoracic and abdominal viscera.
-
The bladder can be seen highlighted in yellow in the illustration.
-
Layers of the urinary bladder wall and cross section of the detrusor muscle.
-
Urinary bladder (black butterfly-like shape) and hyperplastic prostate (BPH) visualized by Medical ultrasonography technique.